In the world of databases, MySQL schema design is like the blueprint for a skyscraper—without it, your data might just end up as a chaotic pile of bricks. If you’ve ever tried to navigate through a tangled mess of tables, you know the importance of a well-structured schema. It’s not just about making things look pretty; it’s about efficiency, speed, and sanity.
Imagine trying to find a needle in a haystack that’s also on fire. That’s what poor schema design feels like. With the right approach, however, you can build a solid foundation that not only organizes your data but also makes it dance to your tune. Get ready to dive into the art and science of MySQL schema design, where creativity meets functionality, and every table has a purpose.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding MySQL Schema Design
MySQL schema design represents the structure and organization of data in a MySQL database. Creating a robust schema involves defining tables, columns, data types, and relationships among the tables. A well-structured schema enhances data integrity and optimizes query performance.
Normalization serves as a key process in schema design. This process reduces data redundancy and ensures that data dependencies make sense. Employing the principles of normalization, such as organizing data into multiple tables, leads to more efficient data management.
Defining primary keys and foreign keys forms another significant aspect of schema design. Primary keys uniquely identify each record in a table, while foreign keys establish relationships between tables. These keys facilitate data retrieval and maintain referential integrity across the database.
Data types play a crucial role in schema design as well. Selecting the appropriate type, such as INT for numbers or VARCHAR for strings, influences both storage requirements and the speed of operations. Appropriate data types minimize the risk of data errors and inefficiencies during operations.
Considering indexing further optimizes schema design. Indexes enhance query performance by allowing the database to locate specific data more quickly. Careful indexing reduces overall query execution time and improves response times for users.
Finally, understanding user requirements is essential in creating an effective schema. Gathering input from stakeholders ensures that the schema design accommodates current needs while allowing for future growth. Balancing flexibility and performance contributes to an optimal schema, meeting evolving data demands.
Key Principles of MySQL Schema Design
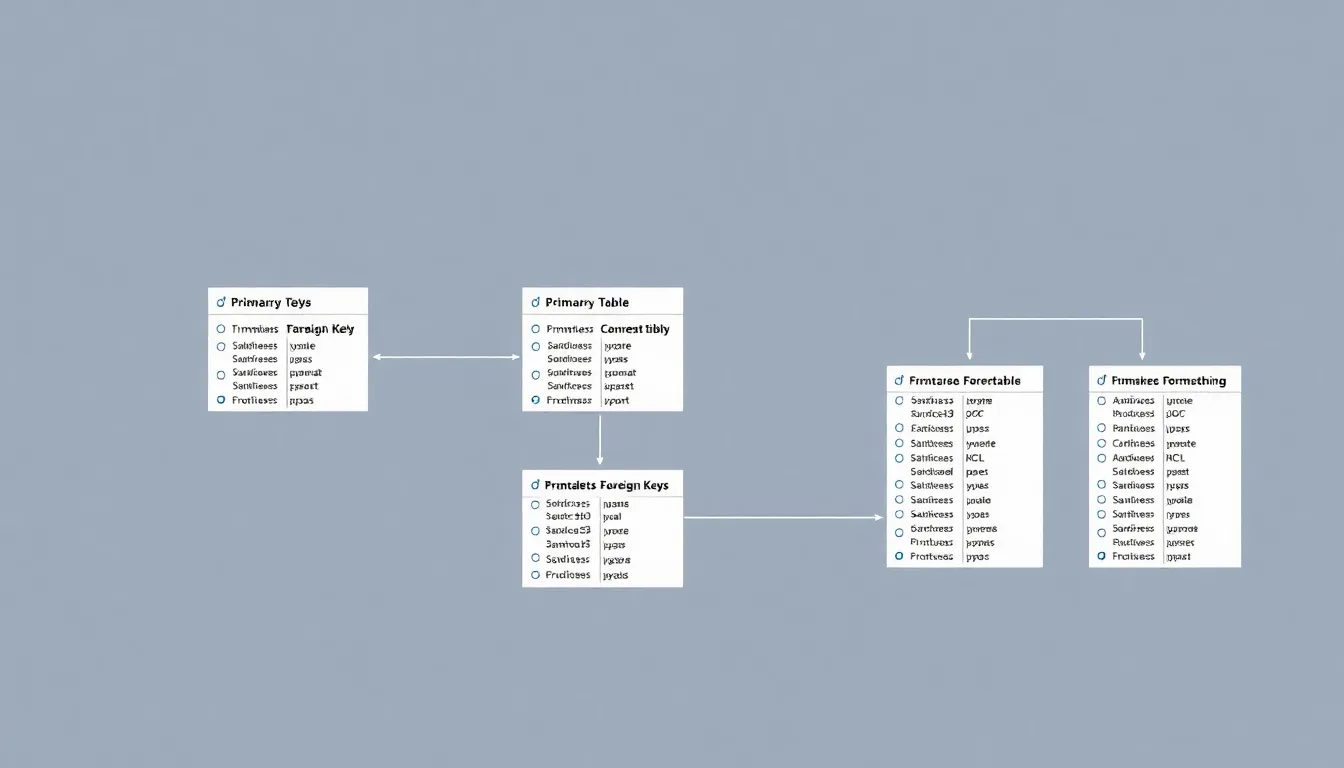
MySQL schema design relies on several key principles that guide database structure and functionality. These principles promote data integrity, efficiency, and usability.
Normalization and Denormalization
Normalization reduces data redundancy and organizes data efficiently. This process involves dividing a database into tables and defining relationships between them, ensuring logical dependencies are maintained. By using normalization, databases can mitigate anomalies during data manipulation. Denormalization, however, serves a different purpose. When performance optimization becomes necessary, denormalization can reduce the number of tables, facilitating quicker access to data. Understanding when to apply normalization or denormalization plays a vital role in schema design, directly influencing query performance and storage efficiency.
Data Types and Constraints
Choosing appropriate data types is critical for maintaining data integrity and enhancing operational efficiency. Different types, such as integers, strings, and dates, each serve distinct functions and influence storage allocation. Constraints, including primary keys, foreign keys, and unique constraints, help enforce rules on data input. Primary keys identify unique records, while foreign keys establish relationships between tables. Beyond enforcing relationships, constraints also minimize input errors, ensuring data remains accurate and reliable. Effectively using data types and constraints can significantly impact overall database performance and usability.
Best Practices for MySQL Schema Design
Effective MySQL schema design employs several best practices to enhance data organization and retrieval. Adhering to these practices ensures higher performance and better maintainability.
Naming Conventions
Choosing clear and descriptive names is crucial for tables and columns. Tables should reflect the data they store, like customers for customer data. Column names must indicate the content, such as using first_name rather than ambiguous labels. Avoiding reserved keywords minimizes confusion during queries. Consistency in naming styles, whether using snake_case or camelCase, promotes readability. Documenting schema elements provides context and aids future developers in understanding the design intent.
Indexing Strategies
Implementing effective indexing strategies significantly boosts query performance. Choosing appropriate columns for indexing is vital, focusing on frequently queried and filtered fields, like email in a user table. Sequential indexes aid in range queries, while composite indexes support multi-column searches. Regularly reviewing and maintaining indexes prevents degradation of performance over time. Additionally, using the EXPLAIN command helps analyze query efficiency, guiding index adjustments when needed. Balancing indexing with write performance remains essential to sustain operational speed.
Common Mistakes in MySQL Schema Design
Designing a MySQL schema involves avoiding several common pitfalls that can affect performance and usability. Ignoring normalization principles often leads to data redundancy, which inflates storage and complicates maintenance. Many designers neglect to define appropriate data types for columns, potentially causing inefficient storage and slow queries.
Failure to establish primary and foreign keys can compromise data integrity, resulting in orphaned records that disrupt relationships between tables. Poor naming conventions also create confusion; unclear names for tables or columns significantly decrease the understandability of the schema.
Inadequate indexing can lead to slow query performance; without proper indexes, data retrieval becomes inefficient, especially with large datasets. Some developers over-index, which can adversely affect write operations and overall performance.
Ignoring user requirements creates schemas that do not meet practical needs, hindering data accessibility and future scalability. Unclear relationships between tables often lead to complex joins, increasing query execution times.
Inconsistent use of constraints can expose databases to invalid data entries, diminishing data quality and reliability. Documenting the schema is crucial; a lack of documentation complicates future modifications and onboarding processes.
Lastly, overlooking the importance of performance testing can result in systems that struggle under real-world workloads. Staying aware of these mistakes enhances the design process, ensuring a robust and efficient MySQL schema.
Tools for MySQL Schema Design
Utilizing the right tools can significantly enhance MySQL schema design accuracy and efficiency. Various software options are available that facilitate schema creation, visualization, and management.
MySQL Workbench offers a comprehensive suite of tools for designing and modeling databases. It allows users to create ER diagrams and perform reverse engineering to visualize existing schemas.
dbForge Studio for MySQL stands out for its versatility. This tool includes a powerful database development interface and allows for database scripting, as well as schema comparison.
SQLyog is another popular choice among developers. It combines database management and design with an intuitive graphical user interface that simplifies schema modifications and management tasks.
HeidiSQL provides a lightweight alternative for creating and managing MySQL databases. Users appreciate its simplicity for editing table structures and navigating the data.
Navicat for MySQL excels with its robust features for database design, development, and administration. It supports code generation and includes visual tools for building schemas via drag-and-drop functionality.
MySQL Schema Visualizer provides a web-based option for creating visual representations of database structures. This tool helps users easily identify relationships and dependencies across multiple tables.
Utilizing these tools streamlines the schema design process, ensuring organization and efficiency. Implementing suitable software improves data integrity, enhances query performance, and simplifies maintenance efforts. Researching and testing various options can lead to identifying the best fit for specific project needs.
Mastering MySQL schema design is essential for anyone looking to create efficient and effective databases. By focusing on principles like normalization and proper indexing, users can ensure data integrity and improve query performance. It’s crucial to understand user requirements and maintain clear relationships between tables to foster usability.
Utilizing the right tools can streamline the design process and enhance accuracy. With a well-structured schema, organizations can not only meet their current data needs but also adapt to future growth. Prioritizing best practices in schema design ultimately leads to a more reliable and efficient database environment.